What our partners say about us
You are likely to be 100% satisfied with the work, with a score of 5.0 being our average.
A presentation on the topic of Customer Journey Map, its application and effectiveness was conducted. In this article, we want to share with you the key conclusions and insights that were obtained during the presentation.
User experience is not just a line in a business strategy. It is the foundation on which any successful product or service is built. The modern world is extremely saturated with information and offers, so customer attention is easy to lose. This is where the need arises for a detailed understanding of user interaction at every stage of their journey — from the first acquaintance with the brand to completing a purchase and further service.
The task of a product designer is to focus on maximum comfort and satisfaction of customer needs, creating a continuous positive experience. In this context, the Customer Journey Map is a tool that allows you to see the entire customer journey, understanding their emotions, behavior, motivations, and pain points.
First of all, it is necessary to clearly understand the existence of different types of methods and how to apply them in the process of research and building a truly high-quality product.
Methods are structured approaches that help teams of designers and developers create products focused on delivering an exceptional user experience.
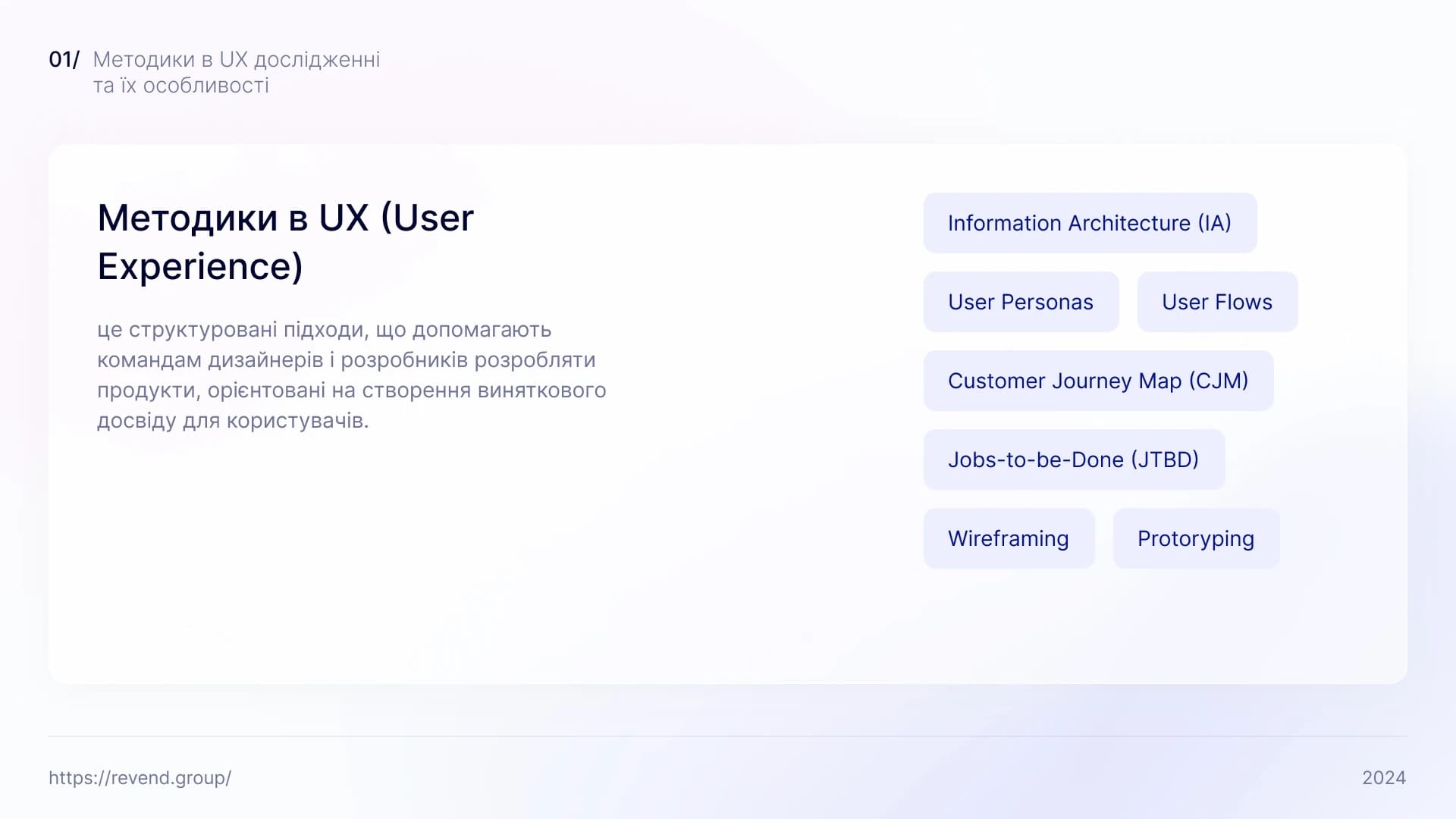
1. Information Architecture: The main purpose is to organize the structure of the product, ensuring a logical relationship between all internal pages.
2. User Personas: Helps us gain a deeper understanding of the characteristics of the target audience in order to create a product that accurately meets its needs.
3. User Flows: Makes it possible to track the user’s path through the product, identifying how they interact with it and achieve their goals.
4. Jobs-to-be-Done (JTBD): Focuses on real user tasks and needs, encouraging the creation of more functional solutions.
5. Customer Journey Map (CJM): Analyzes each stage of interaction with the product to identify strengths and weaknesses and increase user satisfaction.
6. Wireframing & Prototyping: Development of the basic structure and element placement to conduct tests and collect feedback in order to improve the design.
Customer Journey Map not only helps improve the customer experience, but also allows you to understand the customer on an emotional level. In an era where competition intensifies every day, it is no longer enough for businesses to simply offer a high-quality product. It is necessary to provide a unique, pleasant, and flawless brand interaction experience.
And this is exactly what CJM enables, because thanks to it we can:

Customer Journey Map is a visual representation of every interaction a user has with your product or service. But it should be much more than just a diagram. It should immerse you in the details of the user’s emotional states, motivations, pain points, and opportunities for improvement. Every touchpoint is important, as it affects the overall perception of the brand.
The main goal of CJM is to understand how users interact with the product at each stage, starting from the initial contact and ending with achieving their goals, which helps identify opportunities to improve the user experience.

Customer Journey Map is a universal tool that can be applied at any stage of your business life cycle. However, there are key moments when its use brings the greatest value.


Before starting to build a CJM, it is necessary to understand the purpose for which it will be used. This directly affects the research and construction methodology. As a result, you will have two fundamentally different categories.
First, conduct interviews. During interviews with users, it is important to simply ask how they learned about your service and how they receive services. You can use different interview formats — from one-on-one meetings or calls to surveys in Google Forms.
Analyzing the obtained responses will help you identify key touchpoints and improve the user journey overall.
First of all, clearly define business goals and user needs.
Only after conducting multi-level research, and only after that, will it be possible to describe the desired user journey that you plan to guide customers through so that they achieve their goals and satisfy their needs.
Creating a Customer Journey Map may seem like a complex process, but it can be broken down into several clear stages. By completing them sequentially, the result will be an effective tool that helps increase customer satisfaction and product profitability.
The first and most important thing is to clearly understand who your customers are.
A persona is a conditional image of your typical customer based on real data. It is important to create several different personas to cover all audience segments. For example, for an electronics store, you may have different personas for young tech enthusiasts looking for innovations and for older people seeking reliability.
The goal of this step is to reflect the user experience in a specific context of using a particular service in order to better understand their needs, motivations, and behavior. This helps teams create more targeted solutions by adapting the product to user expectations and requirements.
At each stage, the customer interacts with your brand through various touchpoints: advertising, website, social media, email newsletters, customer support, and more.
This step will help you understand when exactly contact occurs between the customer and the service, in order to identify key interaction moments and, of course, the problems that may arise.
The actions a customer takes during each interaction with your brand can be both physical (for example, visiting a store) and digital (browsing products on a website). Understanding these actions will help you better understand where the process can be simplified or improved.
The goal of this step is to begin implementing the user interaction scenario with our service by studying the different stages of the journey that the user goes through. This allows you to identify key touchpoints, improve the experience, and create a holistic picture of how customers perceive our product or service.
Map the environments in which touchpoints occur to understand through which platforms or channels customers interact with the service. By identifying environments, you will be able to clearly understand where exactly touchpoints occur and what processes accompany these interactions.
The purpose of this step should be to gather information about the actions that the customer must perform (or performs) to achieve their goals. This will greatly help you understand the path to successful interaction.
By identifying the user’s goals and needs, you will understand what they are trying to obtain from the service. And by understanding what the user expects to achieve after performing an action, you will be able to properly configure the service to meet these expectations at the wireframe and prototype stages.
Also, note the questions that arise for customers at each step to understand their doubts and needs during the interaction process. But remember, for each action, be sure to record the real thoughts and emotions of users that arise during the performance of actions in order to better understand their experience and feedback.
Each interaction evokes certain emotions in the customer. Do they feel frustration due to a long process of finding the required feature? Or perhaps they are delighted by the speed of problem resolution?
You must describe all obstacles, barriers, problems, and limitations that may prevent the user from achieving the desired result, in order to later eliminate them and create a truly user-friendly product.
Mark both positive and negative emotions, as they determine the overall perception of the brand.
Based on the collected information, you will obtain an overall map, but this is not yet the solution to all your problems. Now you need to think through and propose specific strategies to improve each touchpoint. By identifying barriers, problems, and limitations, you will have ideas for possible solutions and their elimination to increase user satisfaction. These may include recommendations for improving the interface, reducing the time of the entire interaction process, or personalizing content for different customer segments.
Let’s consider a real example of a CJM for an online clothing store that sells youth streetwear:
CJM not only helps understand what the customer does at each stage of their journey. It allows you to dive into the thoughts, emotions, and motivations of the user, which makes it possible to:
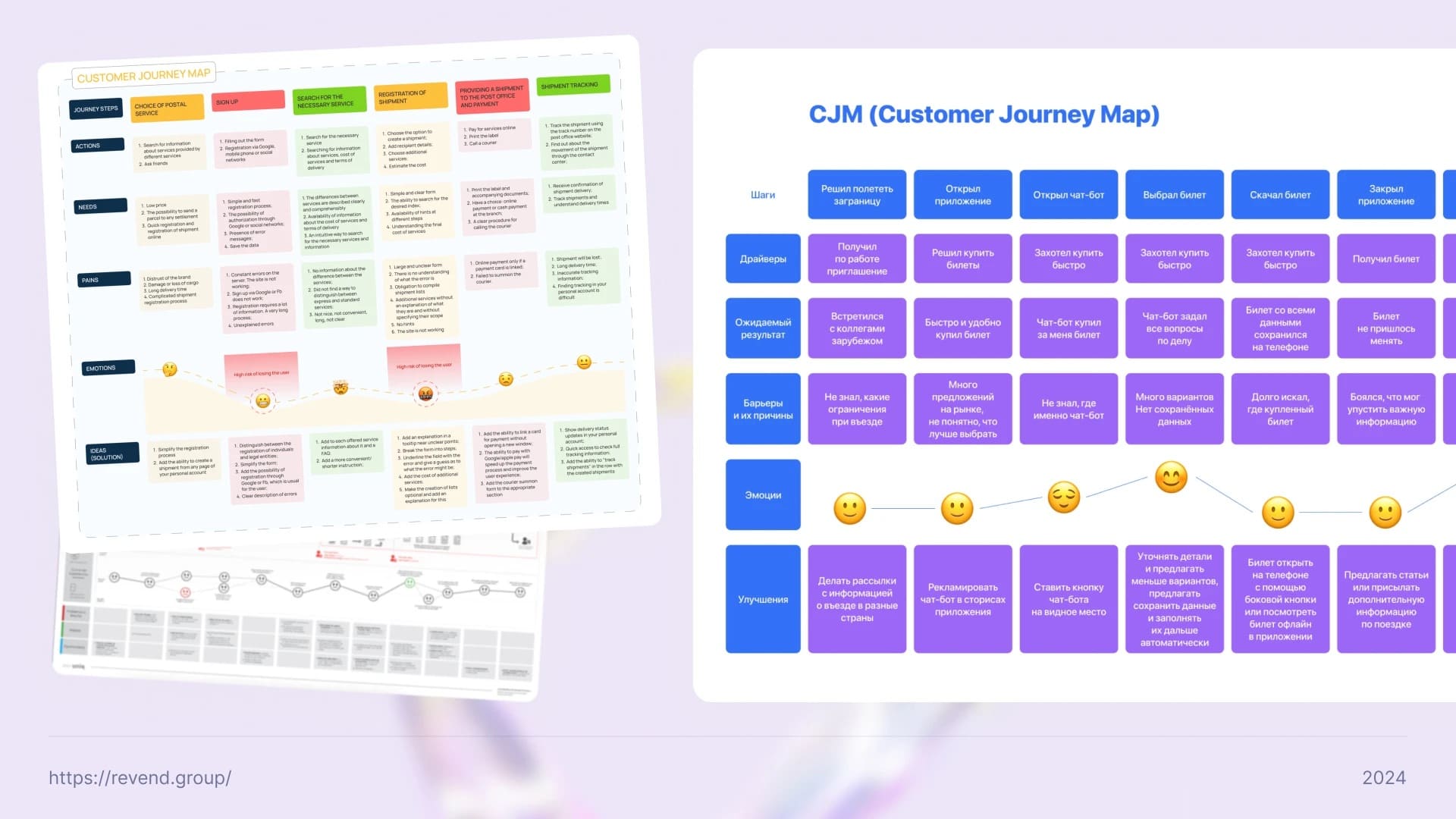
Customer Journey Map allows you to see the entire user journey and create a product that meets real user needs. It is a way not only to understand how customers interact with a company, but also to learn what they think and feel at every stage. Thanks to CJM, we have the opportunity to create products and services that make customers want to return again and again.
We hope that our presentation interested you and helped you better understand the importance of CJM in the modern design world.
If you have any further questions or need a consultation, feel free to contact us.
We strive to be not only a source of information, but also your reliable partner in the world of design and technology. Our team is ready to help you implement your ideas, develop your projects, and achieve great success together.
Thank you for your attention, and see you again!